Child health nursing - Chapter: Growth and Development ▪️ Topic: 1. Definition, principles, factors affecting growth & development, techniques of assessment, plotting of growth chart
Child health nursing -Chapter: Growth and Development
Growth refers to an increase in size and development refers to maturation of function. Starting from conception, growth and development is influenced by various factors both inside the uterus and external environment. Growth and development begin at conception and end at maturity.
Definition of growth and development
Growth is defined as an increase in size of an individual. This increase in size is due to increase in the number and diameter of the cells.
Development denotes the functional maturity of the child. It is the mental maturation with acquisition of skills.
Though growth and development are not the same, they are assessed simultaneously. They are unique characteristics of children and any problem in this process at any stage can result in deviation of growth and /or development.
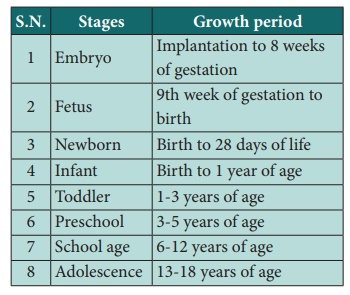
Stages of Growth
The following are the stages of growth in children
Assessment of growth
· Physical anthropometry (weight, height, circumferences of head, chest, abdomen and pelvis)
· Assessment of tissue growth (skin fold thickness and measurement of muscle mass)
· Bone age (x ray of the bone)
· Dental age (by counting the number of erupted teeth)
· Biochemical and histological means.
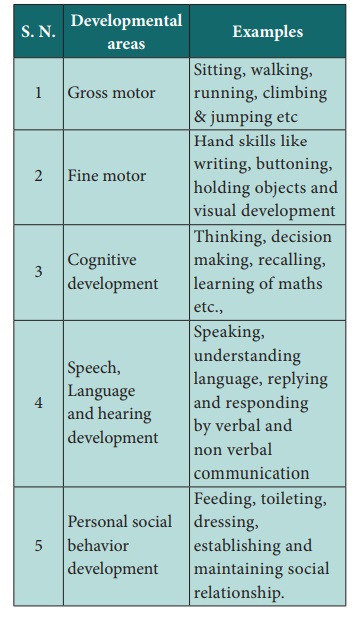
Development can be assessed under various categories. They are
· Motor (gross and fine motor) development
· Speech, Language and hearing development
· Cognitive development
· Personal social behavior development
Principles of growth and development
· Growth is a continuous process
· Growth is an orderly process
· There is period of rapid growth and slow growth
Growth follows a sequence
· Growth proceeds from general to specific
· Head grows faster than the body and extremities
· Growth pattern is same for all children
· Rate of development varies from child to child
· Boys and girls grow differently
Factors influencing growth
Growth is influenced by interaction of both genetic and environmental factors. Children generally grow to their genetic height potential with little outside assistance. Parents have to provide best possible environment for their growth to take place.
Genetic factors: In general, Asians tend to be smaller than Europeans while Afro Americans are taller than white Americans
Parental influence: Tall parents tend to have taller children.
Gender: Boys tend to be taller and heavier than girls
Genetic disorders: Chromosomal disorders such as down syndrome, Turner syndrome and genetic mutations can adversely influence growth.
Post natal (after delivery) growth
Nutrition: Lack of nutrition during first
two years of life after birth has remarkable influence on the growth of the child.
Chronic illnesses in children: Congenital heart diseases, recurrent pneumonia, persistent diarrhea, tuberculosis leads to growth failure.
Hormonal influences: Growth hormone and thyroxin deficiency and sex hormone deficiency during puberty affects growth.
Emotional factors: Emotional deprivation, anxiety may affect the child’s growth.
Developmental mile stones in gross motor functions
Growth Chart
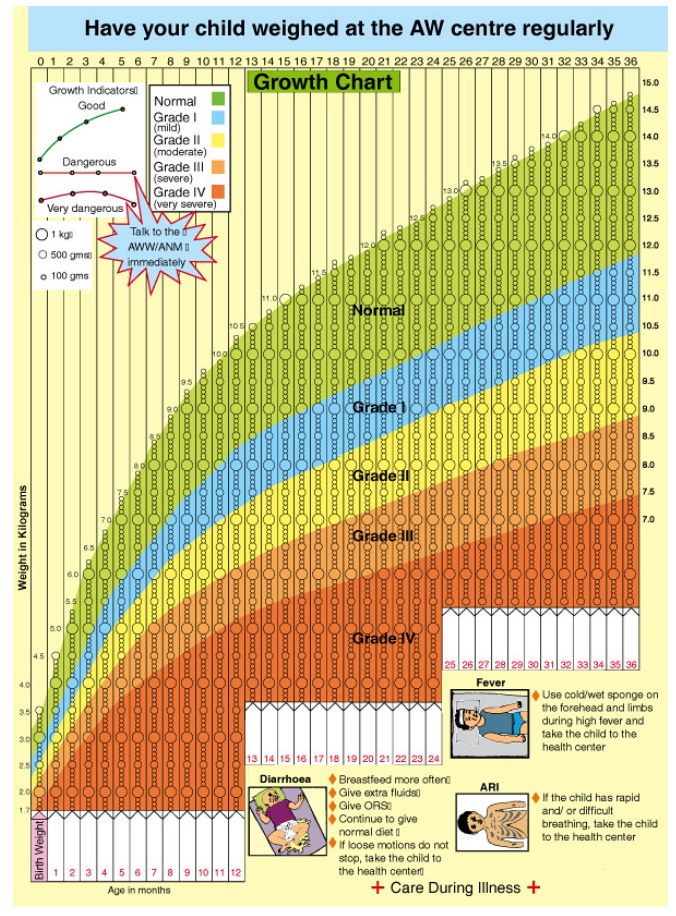
WHO growth chart
Growth chart is developed by Prof. David Morley. It is a visual display of child’s growth and development. In growth chart, child’ weight is recorded periodically and a curve is drawn. A flat curve indicates that the child’s growth is arrested or slowed down. There are reference curves printed in the growth chart. One has to compare the child’s growth curve with the reference curve to detect normalcy or any deviation. There are Height for age and Weight for height chart is available. The various types of growth chart available in India are
· WHO growth chart
· Govt. of India Growth chart
· ICDS growth chart
Uses of growth chart
· To ensure normal growth
· To identify any deviation in growth
· To assess the health status
· To teach mother about the importance of proper care
· To motivate the mother to promote normal growth





Comments
Post a Comment